In one of the class at TU Graz, I learned using a Swizz software called Autoform. The software is expensive but very useful tool. You define your Die, Punch, and Blank by loading your CAD software files, and then define certain properties regarding them in various options in software. The software is easy to use. After pre processing process, the solver makes the calculations for about 5 minutes to reach post processing, and you can then get required simulation of entire deep drawing process. The meshing is automatically generated, and is not very precise as forming processes simulation does not require very fine meshing. You can see the video above, of Simulation I did in Autoform and the important pictures from the simulation process that you can understand just by watching the pictures.
Mechanical Works with fidelity!
Hi! I am Amritpal, I share here, with you, the different mechanical products, Industrial cases, and some tutorials. These are mean to promote mechanical studies around the world.You can ask questions, related to stuff below, by sending me e-mails to metalsonic@live.com.
Tuesday, 10 November 2015
Simulation of Deep Drawing process for sheet metal
In one of the class at TU Graz, I learned using a Swizz software called Autoform. The software is expensive but very useful tool. You define your Die, Punch, and Blank by loading your CAD software files, and then define certain properties regarding them in various options in software. The software is easy to use. After pre processing process, the solver makes the calculations for about 5 minutes to reach post processing, and you can then get required simulation of entire deep drawing process. The meshing is automatically generated, and is not very precise as forming processes simulation does not require very fine meshing. You can see the video above, of Simulation I did in Autoform and the important pictures from the simulation process that you can understand just by watching the pictures.
Wednesday, 7 January 2015
Machining Spur teeth gear on VMC
Here, I received an another machining challenge. The above gears has there centre offset, that means there bores are not in the center of circle, which further means, they can not be machined by hobbing machine, as it requires fixed center of work piece, around which work piece rotate and teeth are cut. So, we decided to machine it on VMC machine, as the gears did not required much precision, or smooth meshing. To do so, we first designed the tooth profile for above gears, then using CAM, we programmed desired tool motion, and the gear teeth were machined. The fibre gears have 39 teeths with 4 module. The end mill used on VMC to machine them was of 3mm diameter.
Thursday, 7 August 2014
Interesting points about Gears
Here are some important points in related to gear technology, which can be pretty useful while designing transmission system which require gears. You can Google and find the definition terms unknown to you.
1. More is the pressure angle, more stronger the gears teeth. 14.5' pressure is mostly used in USA, as they use inches system and calculations become easy for them. 20' is common in Europe and most of the countries in the world. While automobile companies use the pressure angle of 25'.
2. More is the contact ratio between meshed gears, more is the smoothness. Normal Contact ratio is normally 1.6, and is not preferred to use below 1.4 or else very precise arrangement is required between gears centers.
3. Base Circle become smaller than root circle in case of 20' pressure angle gear as the number of teeth increases above 41, which is theoretically proved fact. For 25' pressure angle it is 26 teeth, and for 14' pressure angle gears it is 78.
4. 14' pressure angle have more curvy involute profile of teeth, while the 20' pressure angle teeth are pointy on tip circle.
5. While two gears mesh, there is two type of motion between teeth- sliding and rolling. For good power transmission sliding motion should be minimum, which depends on various factors like teeth finish, lubrication, number of teeth etc. On the pitch circle, the sliding motion is zero, it has only pure rolling motion. As you move further from pitch circle in both radial directions along teeth, the sliding increases.
1. More is the pressure angle, more stronger the gears teeth. 14.5' pressure is mostly used in USA, as they use inches system and calculations become easy for them. 20' is common in Europe and most of the countries in the world. While automobile companies use the pressure angle of 25'.
2. More is the contact ratio between meshed gears, more is the smoothness. Normal Contact ratio is normally 1.6, and is not preferred to use below 1.4 or else very precise arrangement is required between gears centers.
3. Base Circle become smaller than root circle in case of 20' pressure angle gear as the number of teeth increases above 41, which is theoretically proved fact. For 25' pressure angle it is 26 teeth, and for 14' pressure angle gears it is 78.
4. 14' pressure angle have more curvy involute profile of teeth, while the 20' pressure angle teeth are pointy on tip circle.
5. While two gears mesh, there is two type of motion between teeth- sliding and rolling. For good power transmission sliding motion should be minimum, which depends on various factors like teeth finish, lubrication, number of teeth etc. On the pitch circle, the sliding motion is zero, it has only pure rolling motion. As you move further from pitch circle in both radial directions along teeth, the sliding increases.
Wednesday, 14 May 2014
Machining Sprocket on VMC instead of Hobbing: Designing and Machining
I previously posted on how to model a Sprocket profile on your design software which I made on Pro/E. Now, Sometime the requirements of machining a bigger module sprocket exceed your hobbing machine capability to machine it for heavy standard chains.In those cases, you can model the sprocket's teeth profile, and make the program for your VMC machine using cam softwares, as the profile of teeth are pretty complicated. For example, below is the sprocket made on VMC, which took same time as it taked on manual hobbing machine. It costs a little more but when your hobbing fails this can be the other option!
A Perfect curve on the teeth is achieved...
Now, You can check sprocket made these ways for standard chains and will find good results, as I checked them below for the sprockets of different PCDs for standard chains
Saturday, 15 March 2014
Tapered shaft lock :-Shaft Couplers (Transmission)
These are kind of locking device used as key-less shaft
coupling. They are assembled to transmission components like gears, pulleys,
timing pulley, as bushes etc. generally, where no play is must for the
transmission between shaft and transmission element. The main applications of
these are in CNC machines, which are very precise. Today, because of intense
pressure to maximize uptime, precision, and efficiency while minimizing
material, machining, and operating costs, key-less frictional locking devices
are the hot trend. The basic idea is similar to a clamp coupling but the moment
of rotation is closer to the centre of the shaft. In traditional keys, there
were possibilities of worn out, which are removed by using these coupling
devices. It is more robust than using a key because maintenance only requires
one tool and the self-centering balanced rotation means it lasts longer than a
keyed joint would, but the downside is that it costs more. Below, I have added some pictures of these,
used in timing pulleys, from which you can get an idea of how to assemble them.

So here, I have these 2 screws, which tight the lock using L key. There is also a long single screw, which is just right on the other-side of staring line opening, which is used to disassemble or take out the nut from timing pulley. These are available in the market in standard sizes at cheap prices.
Thursday, 6 March 2014
Fool's Play :- Pulley lift system (Mechanics)
Lifting heavy loads are very common in the industries.For example, lifting weights of products being manufactured are quit common in factories. Now while designing such lifting machines, a designer may face various constraints, which can restrict his choice to use heavy power machine elements like motors or actuators to deal with such loads.
Here is an very simple, cost effective trick, which is, by using pulley and wire rope system to divide the weight into various wire rope connections, resulting in reduction in load for actuators or motors to lift the same weight. But the actuator or motor has to pull rope for longer distance though. Diagram given below, explain it quit well.
W= Weight, T= Tension , F= Force in Newtons, H= Height.
All you need is :
1. A wire rope , which can be standard and can be chosen according to the weight to lift.,
2. A Sheave ( Pulley), which is also available as standard part and is chosen according to wire rope chosen,
3. And then you need a shaft, bearing, sheet-metal housing and nuts to make the coupling.
Various other ways to make pulley connection according to space constraints are given below:
Monday, 17 February 2014
FEA Analysis (Using Hyperworks and Ansys)
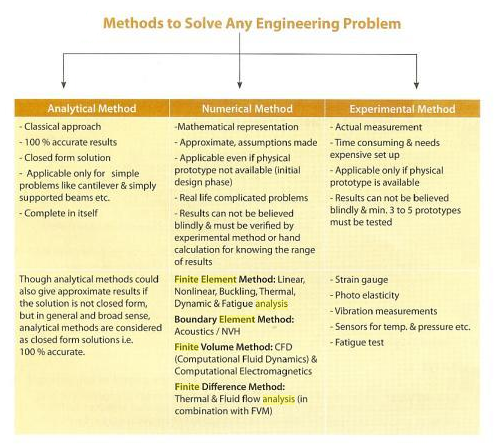
To analyse, the maximum stress and strain, a machine or machine components can face, it become very hard to make calculations by conventional formulas, of stress and strain, while making calculations for complex geometrical shapes, made up different materials, complex loading varying with time etc. For example, to calculate the stress at any point of engine body, it would take months to make calculations by using various formulas. Now, that technique is called scientific approach toward the problem, also called Analytical Method. In the beginning of 20th century, mathematicians developed various Numerical Methods, which make problem solving faster, though gives you a solution correct upto about 90%, unlike Analytical methods which gives a 100% correct solution. In the Industry, time is a very important aspect in the development of project or product. Now for example, To develop a product, in least time, Analytical methods would make calculations very long, and thus would make it hard to achieve goals in time. Thus for that purpose, Industry uses Numerical methods to make calculation of various forces while developing a product, which are fast, even though they are not as much accurate as analytical methods, as Industry can compromise a accuracy of about 10% before time. The product is made by approximations, and assumptions, and the results achieved by numerical methods can not be trusted blindly, and thus, they make prototypes and test experimentally, by experimental methods in the company's protoshops. If prototype passes,the product drawings are finalized and are released. The various methods and various Numerical methods, which are of our main concern, are discussed below briefly.
I have been providing, random mechanical studies. I have decided to make a new blog about FEA Analysis, in which I will give complete knowledge about the subject of Strength of Materials, Finite element methods, and use of software to make calculations even more faster, by Hypermesh and Ansys. The Finite element method, in Numerical methods, solves a problem, lets say a stress analysis on big sheet metal surface, by dividing the sheet metal part into many small parts, in the form of quads and trias, made of nodes, and those small parts are called elements. By dividing into small parts by a process called meshing, the stresses in each elements are calculated, and are added up to achieve the final solution.
Now, the small parts called elements can be in large amounts, resulting in large calculations to be made and we use computer softwares to make large calculations easy. I will soon update you with my new blog about FEA Analysis, as soon I make it.
Now, the small parts called elements can be in large amounts, resulting in large calculations to be made and we use computer softwares to make large calculations easy. I will soon update you with my new blog about FEA Analysis, as soon I make it.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)